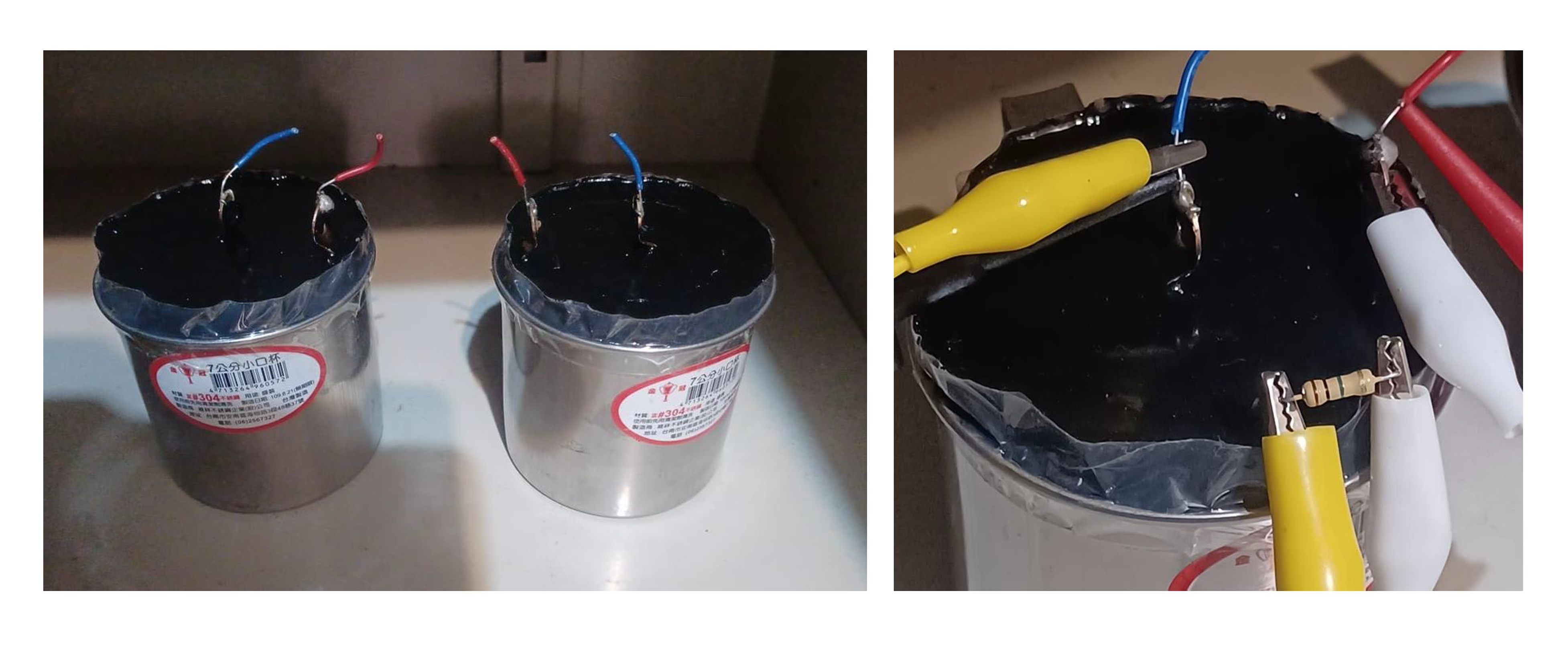
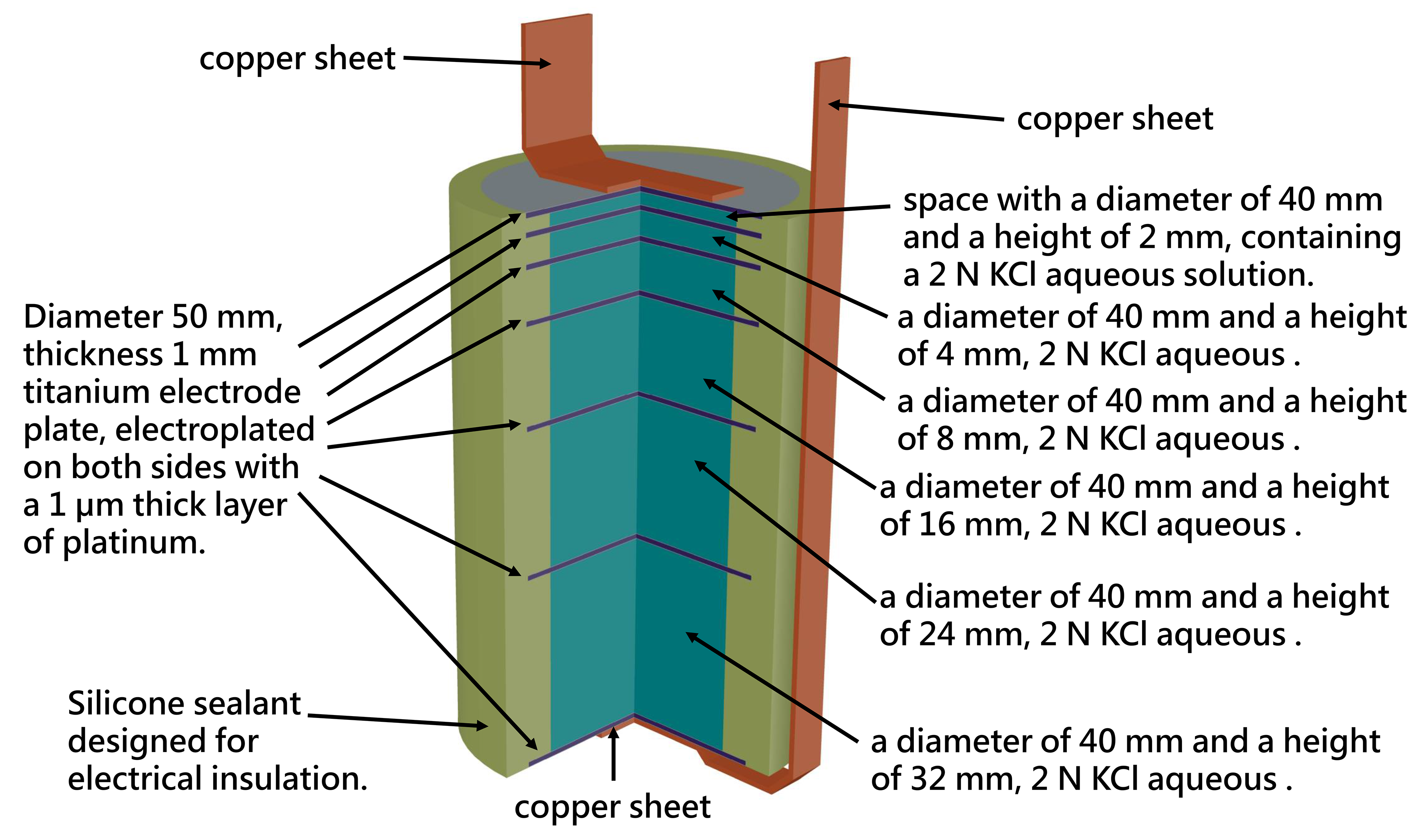
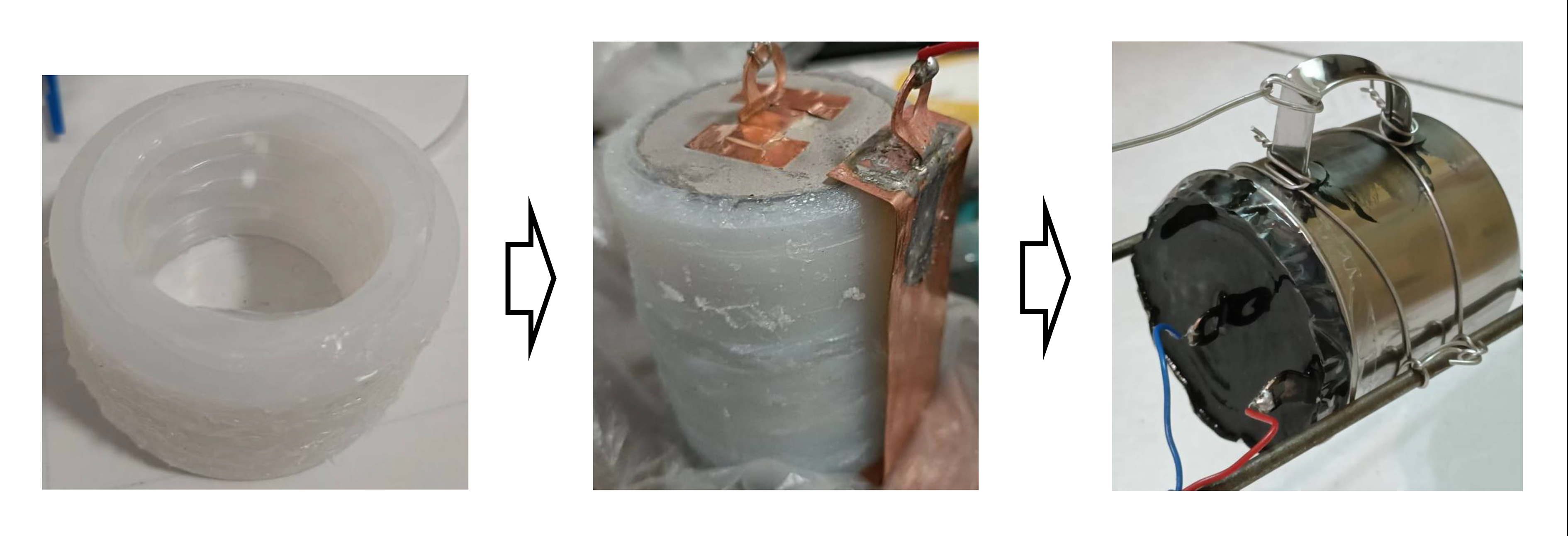
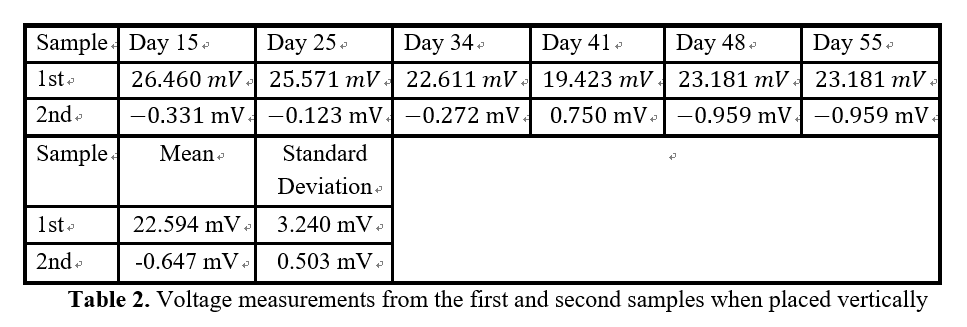
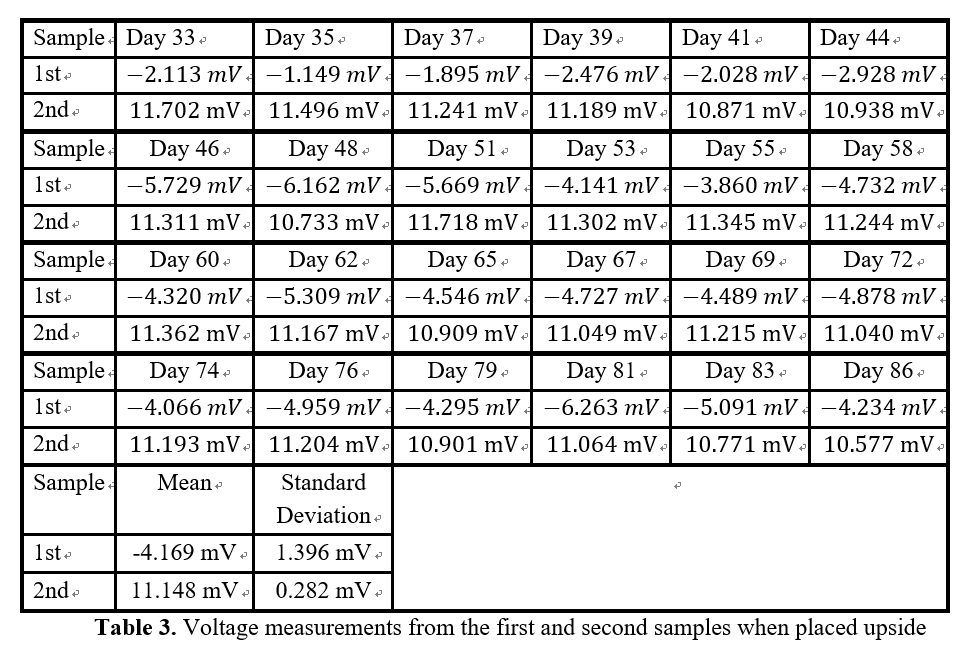
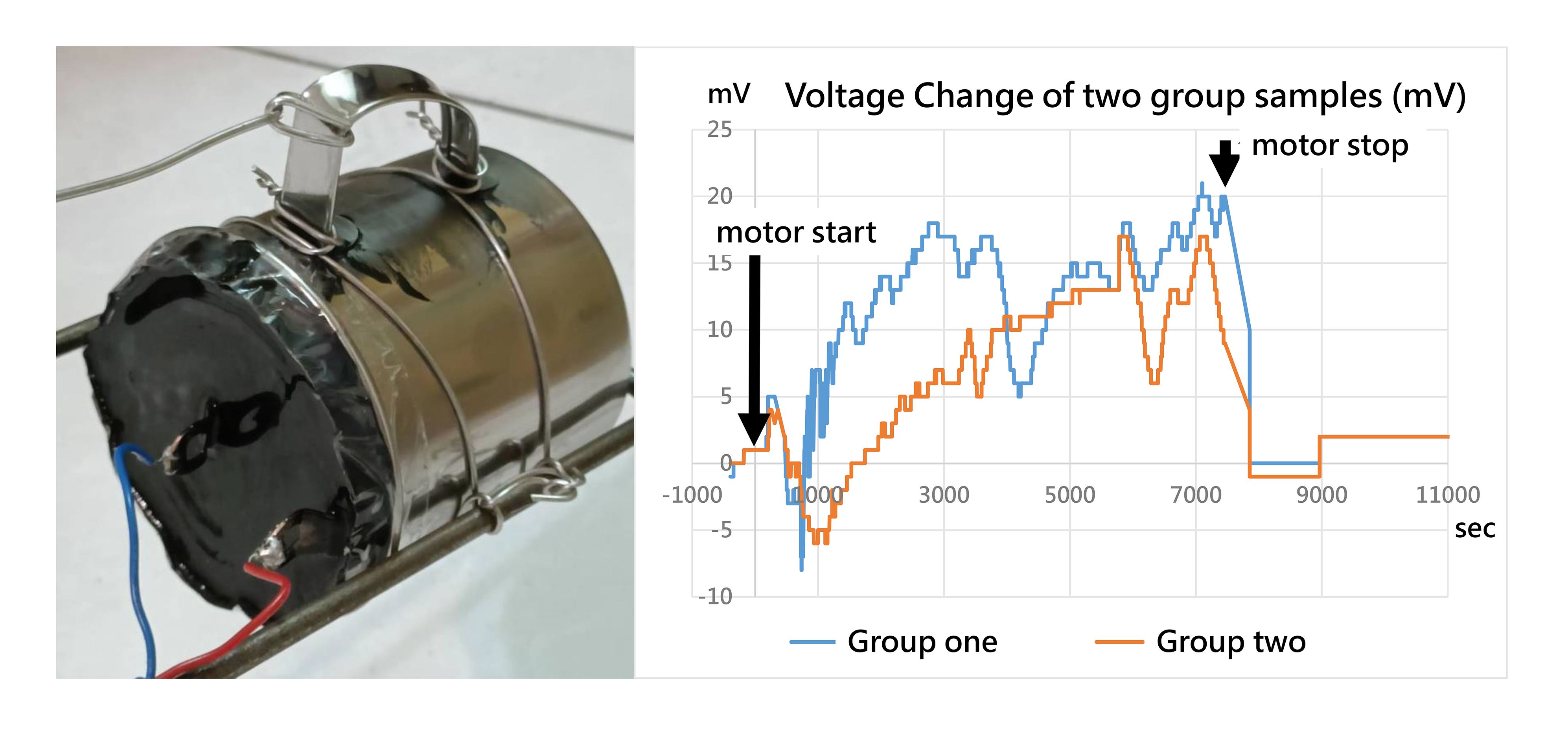
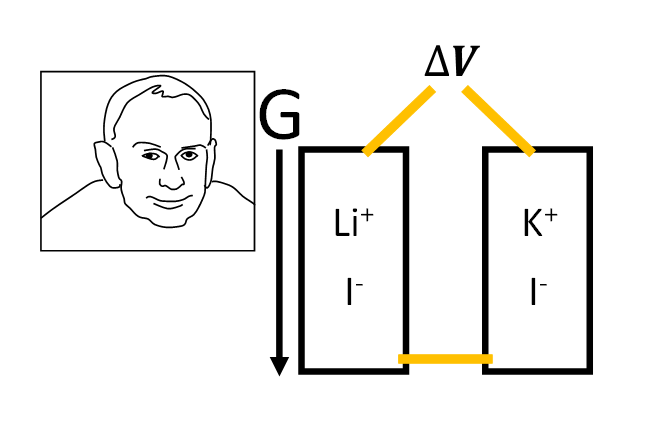
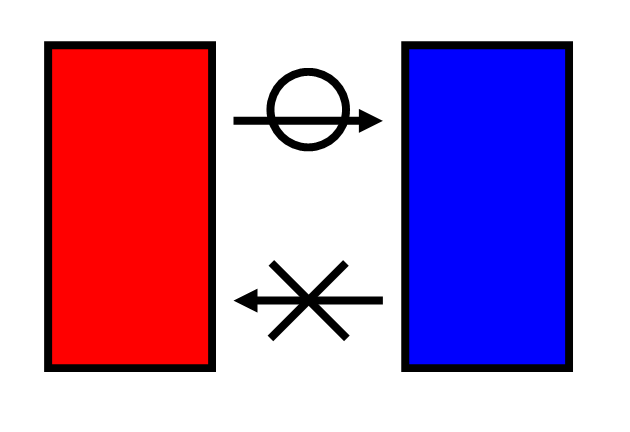
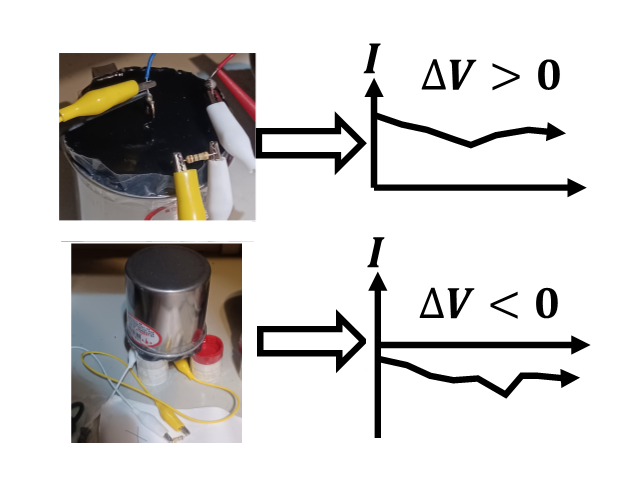
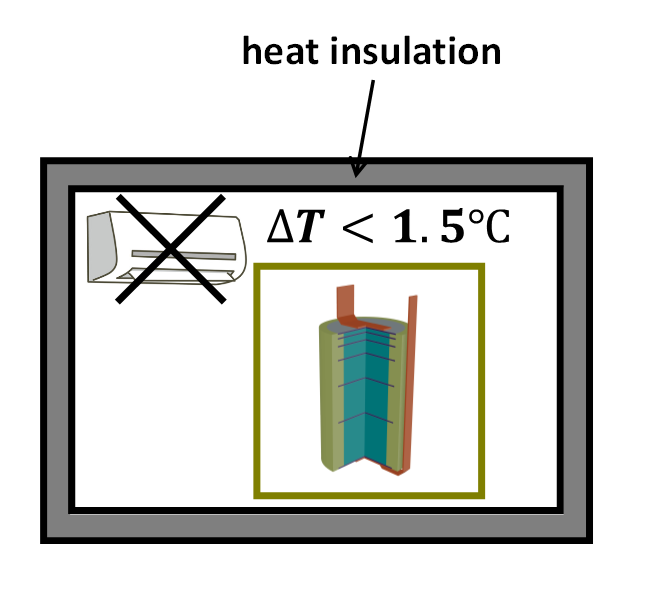
Gravitational Field Ion Separation
Spontaneous charge separation driven by mass difference
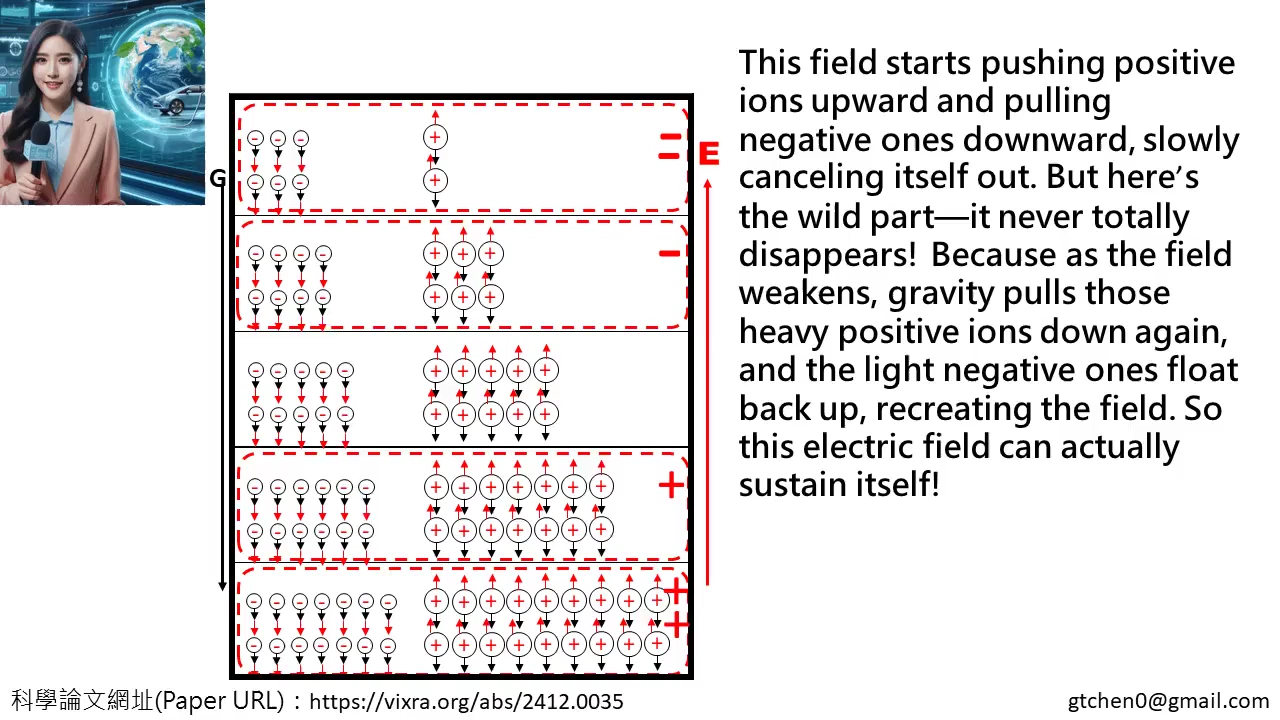
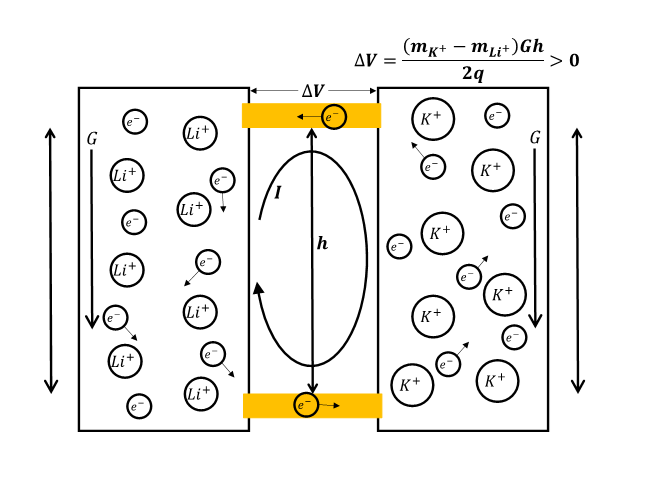
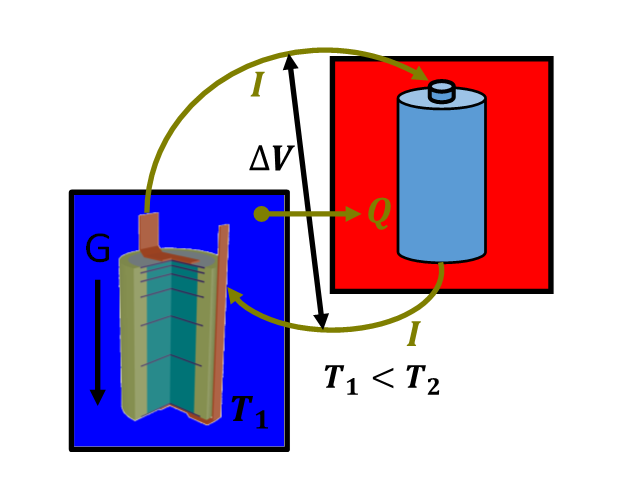
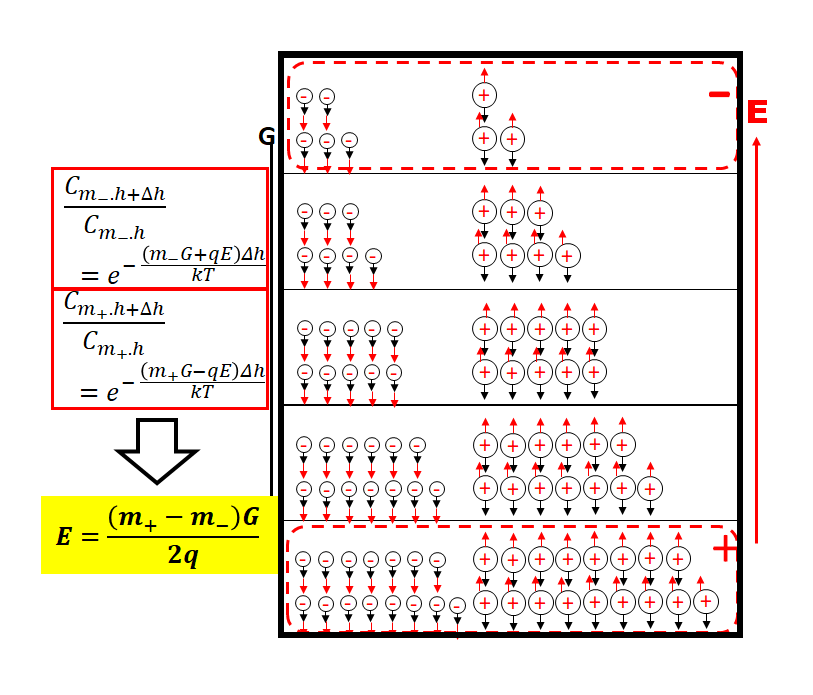
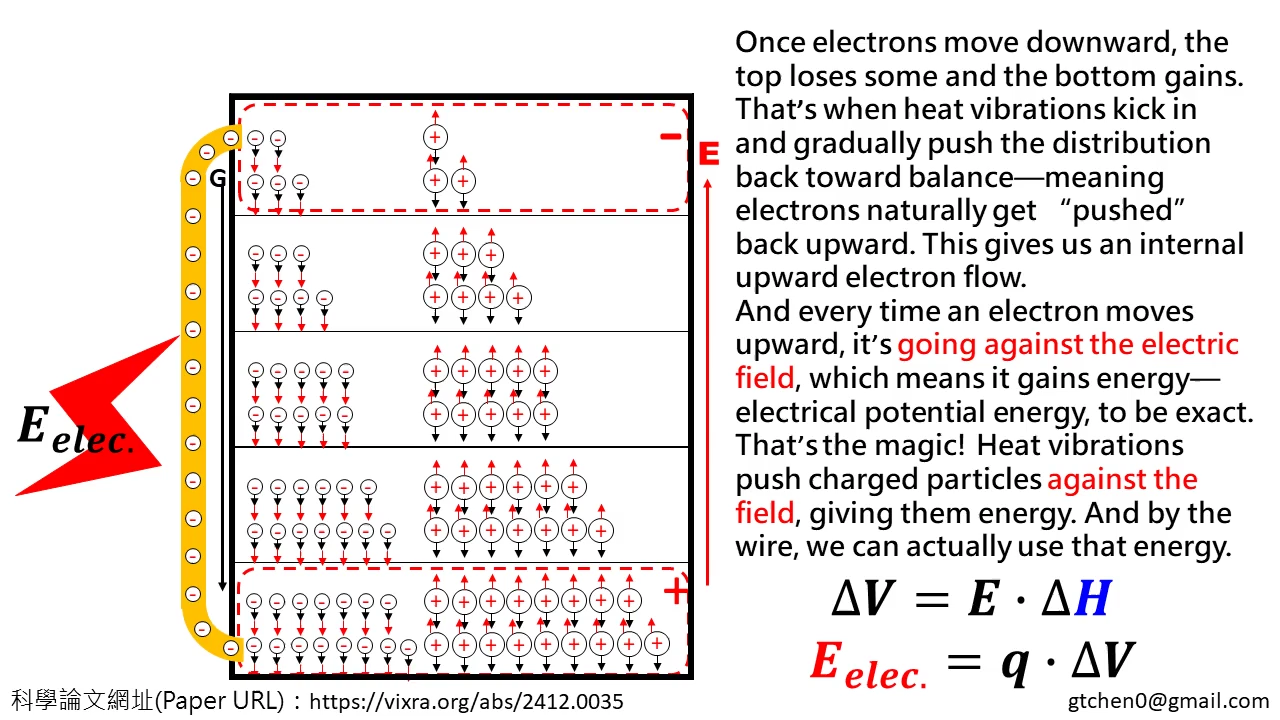
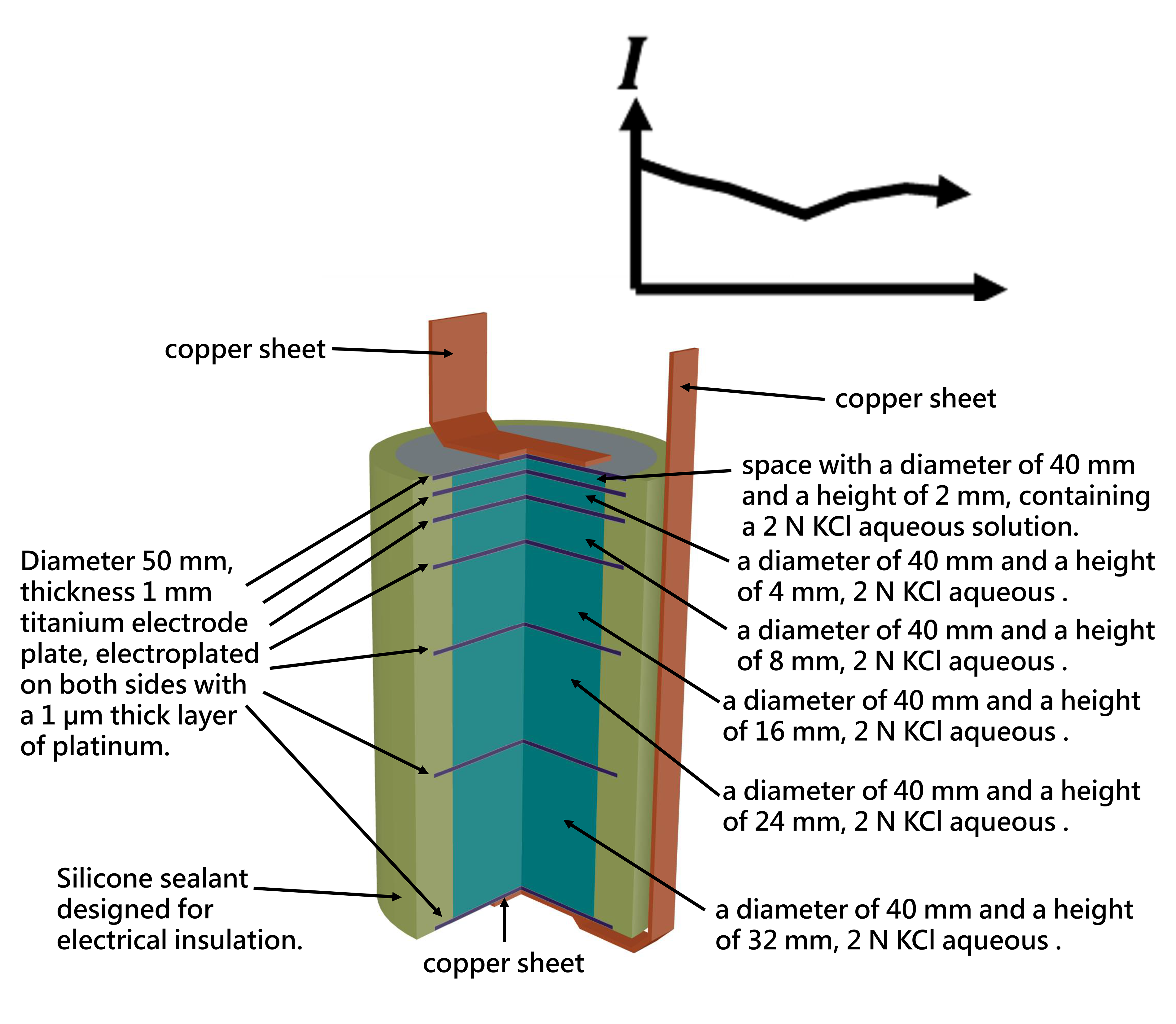
Under gravitational field influence, ions with different masses exhibit distinct spatial distribution differences. Heavy ions tend to settle to the bottom, while light ions float to the top, forming a concentration gradient distribution.
When charged ions replace neutral molecules, this mass-difference-induced separation phenomenon creates charge imbalance, spontaneously forming a stable electric field distribution.
Key: The greater the mass difference, the more pronounced the charge separation effect